DataMotion™ Achieves Full DirectTrust™ HISP Re-Accreditation
Accreditation ensures compliance with DirectTrust HISP Policy requirements and interoperability with conforming HISPs
WASHINGTON, DC and Florham Park, NJ, January 20, 2020 – DataMotion today announced it has achieved full re-accreditation through the DirectTrust™ Accreditation Program for Health Information Service Providers (HISPs). DirectTrust is a non-profit healthcare industry alliance created to support secure, identity-verified electronic exchanges of protected health information (PHI) between provider organizations, and between providers and patients, for the purpose of improved coordination of care.
Founded in 1999, DataMotion today has millions of desktop, tablet and mobile users that leverage its mature, cloud-based secure data exchange platform and services, many for health care applications. In the fall of 2012, the company expanded operations as a HISP and introduced DataMotion Direct. The company achieved its first EHNAC HISP accreditation in 2013, and added the CA and RA accreditation in 2014. Today’s announcement signifies the DirectTrust HISP accreditation renewal, and an ongoing commitment to the increasing adoption and expansion of the Direct Secure Messaging network.
DataMotion HISP services software were audited against a series of technical, physical, and operational criteria and found to be fully in compliance with the Direct Standard™ and the requirements of the DirectTrust Security and Trust framework.
“DirectTrust HISP accreditation certifies that an organization has established and upheld a superior level of trust for its stakeholders, which is a significant distinction. Kudos to DataMotion’s commitment to maintaining the highest standards in privacy, security and confidentiality,” said DirectTrust President and CEO, Scott Stuewe.
“Renewal of our accreditation with DirectTrust demonstrates our commitment to secure, interoperable clinical health information exchange across the care continuum using Direct Secure Messaging,” said DataMotion co-founder and CEO Bob Janacek. “Leveraging our population-scale cybersecurity platform as a service (PaaS), DataMotion Direct allows mHealth apps to aggregate and analyze longitudinal data from disparate ambulatory and acute systems, reduce costs and improve clinical outcomes.”
About DirectTrust Accreditation Program for Health Information Service Providers
The DirectTrust Accreditation Program recognizes excellence in health data processing and transactions, and ensures compliance with industry-established standards, HIPAA regulations and the Direct Standard. Launched in March 2010 as a part of the Nationwide Health Information Network, the Direct Project was created to specify a simple, secure, scalable, standards-based way for participants to send authenticated, encrypted health information directly to known, trusted recipients over the Internet. Today DirectTrust is an American National Standards Institute accredited Standards body and the custodian of the Direct Standard.
DirectTrust participating organizations are evaluated in the areas of privacy, security and confidentiality; technical performance; business practices and organizational resources as they relate to participants in the DirectTrust network and other Direct Secure Messaging participants. Additionally, their process of managing and transferring protected health information is assessed and determined to meet or exceed all DirectTrust criteria and industry standards. Successful completion of the Accreditation Program demonstrates organizations’ adherence to strict standards and participation in the comprehensive, objective evaluation of their business.
About DirectTrust
DirectTrust is a non-profit, vendor-neutral alliance initially created by and for participants in the Direct community, including Health Information Service Providers (HISPs), Certificate Authorities (CAs), Registration Authorities (RAs), doctors, consumers/patients, and vendors. DirectTrust serves as a forum for governance, and accreditation body for persons and entities engaged in exchange utilizing the Direct Standard™, supported by DirectTrust’s robust security and trust framework. The goal of DirectTrust is to develop, promote, and, as necessary, help enforce the rules and best practices necessary to maintain security and trust within the Direct Secure Messaging community. DirectTrust is committed to fostering widespread public confidence in the interoperable exchange of health information. To learn more, visit www.directtrust.org.
Media Contact:
Ed Emerman
Eagle Public Relations
609.275.5162
eemerman@eaglepr.com
About DataMotion
Since 1999, DataMotion secure data exchange technology has enabled organizations of all sizes to reduce the cost and complexity of delivering electronic information to employees, customers and partners in a secure and compliant way. Ideal for highly regulated industries, the DataMotion portfolio offers easy-to-use, CX friendly, encryption solutions for email, file transfer, forms processing and customer-initiated contact. In the healthcare sector, DataMotion is an accredited HISP (health information service provider), Certificate Authority (CA) and Registration Authority (RA) of Direct Secure Messaging. The DataMotion Direct service enables efficient interoperability and sharing of a person’s data across the continuum of care and their broader lives. DataMotion is privately held and based in Florham Park, N.J. For the latest news and updates, visit https://datamotion.com/, follow DataMotion on LinkedIn or Twitter® @datamotion.
Contact:
Monica Hutton
Marketing Director
DataMotion
973-455-1245
monicah@datamotion.com
# # #

















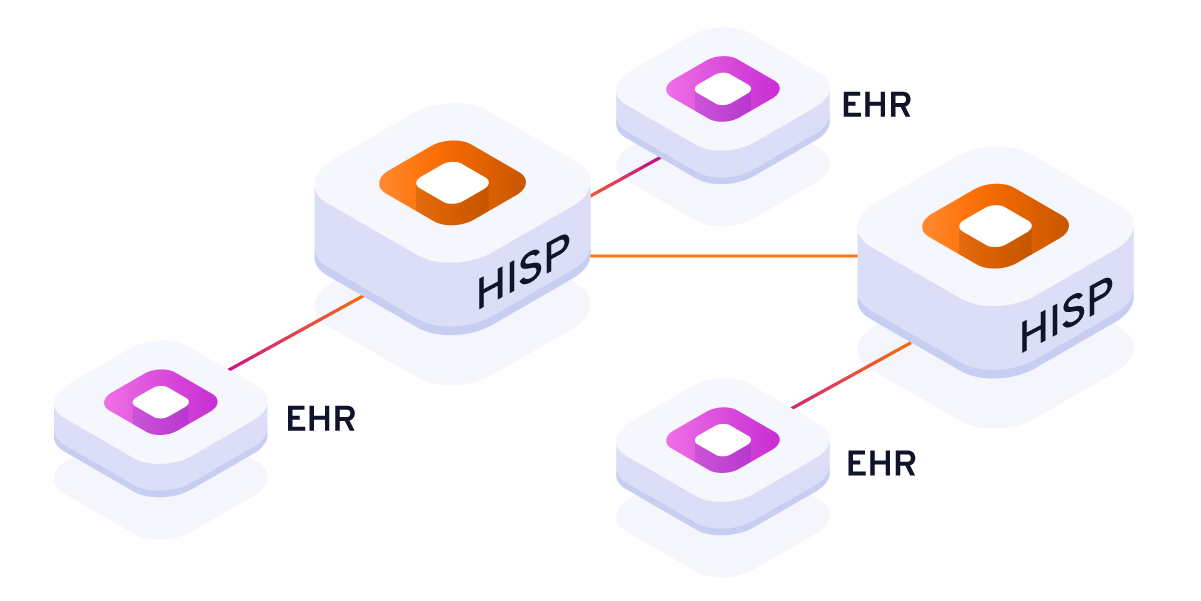
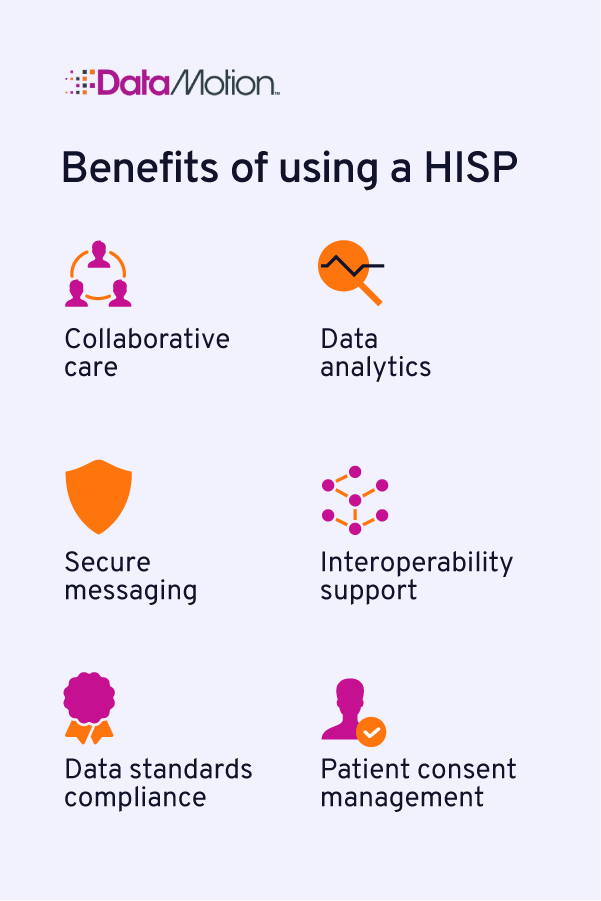 Collaborative care: When patients need treatment from other providers and specialists, the relevant healthcare professionals can send their information and medical history accordingly. Additionally, professionals can log patient health information on systems like health information exchanges (HIEs), allowing any healthcare facility to access common health records.
Collaborative care: When patients need treatment from other providers and specialists, the relevant healthcare professionals can send their information and medical history accordingly. Additionally, professionals can log patient health information on systems like health information exchanges (HIEs), allowing any healthcare facility to access common health records.